Fundamentals of an Optical Module
As an important part of fiber-optic communication, an optical module is a photoelectric converter which converts electrical signals into optical signals and vice versa.
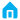
An optical module works at the physical layer of the OSI model and is one of the core components in the fiber communication system. It mainly consists of optoelectronic devices (optical transmitter and optical receiver), functional circuits, and optical bores. Its main function is to convert between electrical and optical signals during optical signal transmission. Figure 1-1 shows how an optical module works.
The transmit optical bore inputs electrical signals at a certain bit rate, which are then processed by the internal driver chip. After the processing, the drive's semiconductor laser diode (LD) or light emitting diode (LED) emits modulated optical signals at the corresponding rate. When the optical signals reach the receive optical bore through an optical fiber, they are converted back into electrical signals by the photodetector diode. The electrical signals are then output at the corresponding bit rate after passing the preamplifier.
Figure 1-1 Working principle of an optical module

Appearance and Structure of an Optical Module
There are various types of optical modules, and their appearances and structures are different. However, the basic structure of an optical module includes some common parts, as shown in Figure 1-2.
Figure 1-2 Appearance and structure of an optical module (using an SFP optical module as an example)


What Are the Common Types of Optical Modules?
Classification by Transmission Rate
To meet various transmission rate requirements, optical modules with different rates are provided, including 400GE, 100GE, 40GE, 25GE, 10GE, GE, and FE optical modules.
Classification by Form Factor
A higher transmission rate depends on a more complex structure. Different form factors in different structures are provided for varying transmission rates. switches support optical modules of the following form factors: Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP)/Enhanced Small Form-factor Pluggable (eSFP), SFP+, SFP28, Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus (QSFP+), 120 Gb/s eXtended-capability Form Factor Pluggable (CXP), Centum Form-factor Pluggable (CFP), QSFP28, and QSFP-Double Density (QSFP-DD).
Classification by Mode
Optical fibers are classified into single-mode and multimode fibers. Therefore, optical modules are also classified into single-mode and multimode modules to support different optical fibers.
- Single-mode optical modules have a typical center wavelength of 1310 nm or 1550 nm, and are used with single-mode fibers. Single-mode fibers support a wide band and large transmission capacity, and are used for long-distance transmission.
- Multimode optical modules have a typical center wavelength of 850 nm, and are used with multimode fibers. Multimode fibers have lower transmission performance than single-mode fibers because of modal dispersion, but are more cost-effective. They are used for small-capacity, short-distance transmission.
Classification by Center Wavelength
The operating wavelength of an optical module is a range. To facilitate description, the center wavelength is used, in unit of nm.
To support transmission of optical signals in different optical bands, optical modules with different center wavelengths, such as 850 nm, 1310 nm, and 1550 nm, are provided.
Classification by Light Color
The biggest difference between colored optical modules and other types of optical modules lies in the center wavelength.
- Generally, the center wavelength of an optical module can be 850 nm, 1310 nm, or 1550 nm. The center wavelength of an optical module is simple, and the light is called gray light.
- A colored optical module carries light with different center wavelengths. This type of light is called colored light.
Colored optical modules are classified into two types: coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM) and dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM). Within the same band, DWDM modules are available in more types and use wavelength resources more efficiently than CWDM modules. DWDM and CWDM modules allow lights with different center wavelengths to be transmitted on one fiber without interfering each other. Therefore, a passive multiplexer can be used to combine the lights into one channel, which is then split into multiple channels by a demultiplexer on the remote end. This reduces the optical fibers required. DWDM and CWDM modules are used for long-distance transmission.
Category (Example)
According to the preceding classification, the following table lists the types of some common optical modules based on different features.
Table 1-3 Examples of common optical module types
|
Feature
|
SFP-GE-LH40-SM1310
|
SFP-10G-ER-1310
|
QSFP-40G-LR4
|
QSFP-100G-CWDM4
|
QSFP-DD-400G-SR8
|
| Rate |
GE |
10GE |
40GE |
100GE |
400GE |
| Form factor |
eSFP |
SFP+ |
QSFP+ |
QSFP28 |
QSFP-DD |
| Mode |
Single-mode |
Single-mode |
Single-mode |
Single-mode |
Multi-mode |
| Center wavelength (nm) |
1310 |
1310 |
1271, 1291, 1311, 1331 |
1271, 1291, 1311, 1331 |
850 |
| Light color |
Gray light |
Gray light |
Gray light |
Colored |
Gray light |
So why wait? Contact Dawnergy today to learn more about our range of Optical Modules and start enjoying the benefits of cutting-edge technology today!

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!